What is a Thermocouple?
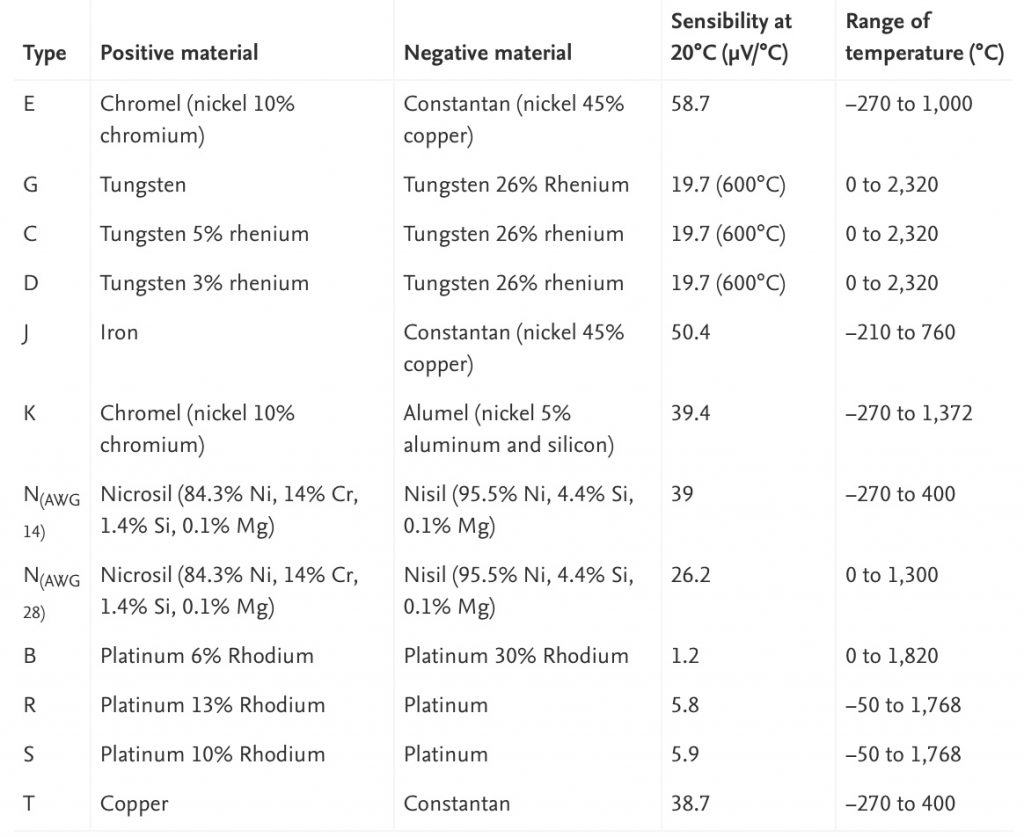
Thermocouples are electronic sensors, used for temperature monitoring. Thermocouples come in different grades or types. The two most common are the J-type thermocouple and K-type thermocouple. There are however several others. Type T, N, E, B, R, and S. J, K, T, and E types are known as “base metal thermocouples” and are more common. R, S, and B are made from Noble Metals. They are used in very high-temperature applications. The below table illustrates the different Thermocouple types, their composition, and temperature ranges.
How Do Thermocouples Work?
A thermocouple converts temperature to a small DC Voltage. As you can see from the above table, they consist of two dissimilar metal wires that meet in two or more places. The output voltage changes in a linear manner with the temperature difference between the two junctions. When the temperature is high, the greater the DC Voltage output. It is a good practice to protect your thermocouple with a suitable coating or tube. Typically a metal coating or a ceramic tube is used to protect the thermocouple wires from damage.
What is a K Type Thermocouple?
The K-type thermocouple is probably the most common type. its low cost and relatively good accuracy together with a wide temperature range make it a versatile sensor. They are suitable for continuous exposure to temperatures around 1,100°C, with a max temp of 1,372°C (-328°F to 2,501°F).
Different thermocouple types utilize various metals for their positive and negative wires. K-type thermocouples are nickel-based, and therefore also have good resistance to corrosion. This makes them suitable for use in oxidizing atmospheres. K-type thermocouples utilize Chromel, Nickel-Chromium (10% chromium) for the Positive leg. The Negative leg is Alumel, Nickel-Aluminium (5% aluminum). The accuracy of a K-type Thermocouple is typically a maximum of +/- 2.2°C or +/- 0.75%, whichever is greater. However, there can be differences between different thermocouples, ven coming from the same production batch due to deviations in the alloys. It is therefore recommended that thermocouples undergo individual calibration.
K-type thermocouples are found in use for many industries such as water, chemical and gas, and food industries. They are one of the more inexpensive thermocouples with good resistance to oxidization, god linearity of measurement, and stability.
What Are K Thermocouples Used For?
They’re generally employed in applications when the temperature is above 550°C and the thermocouple’s maximum operating pressure is reached.
- They are used in many industries like Steel & Iron to monitor temperature & chemistry throughout the steelmaking process
- Used for testing temperatures associated with process plants e.g. chemical production and petroleum refineries
- Used for testing heating appliance safety
- Type K is commonly used in nuclear applications because of its relative radiation hardness.
K Type Thermocouple Accuracy
K-type thermocouples are only stable for short periods of time at specific temperatures. They have a tendency to drift in a positive direction. The amount of drift is dependent on the temperature they are exposed to. For example, the higher the temperature, the greater the drift. At 1,000°C the readings may be off by as much as 5°C. Prolonged exposure above 427°C accelerates the aging of the thermocouple.
K Type Thermocouple Junctions
There are different methods for joining the positive and negative wires.
Grounded Thermocouple Junction
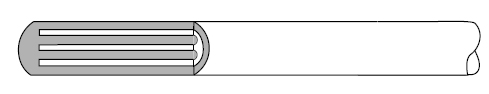
This is the most common type of junction. In this type, both the thermocouple wires and the sheath are welded to make one junction at the tip of the probe. The grounded junction type thermocouples have excellent response time due to the thermocouple making direct contact with the sheath.
ungrounded Thermocouple Junction

The thermocouple is ungrounded when the positive and negative wires are welded together but insulated from the sheath.
Exposed or “Bare Wire” Thermocouple Junction

In an exposed type thermocouple, the wires are welded together and directly inserted into the handle. These thermocouples have a very fast response time but are more prone to damage, corrosion, and degradation as there is no sheath protecting them.
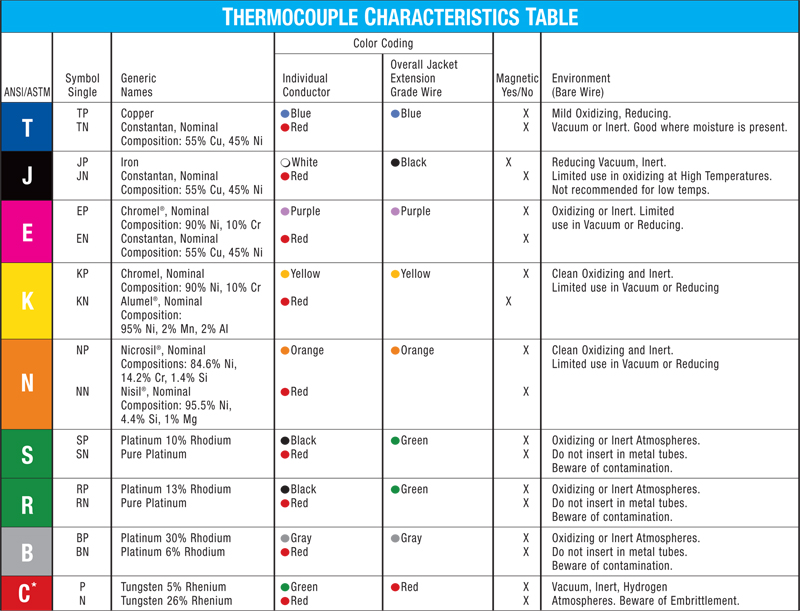
Thermocouple Color Coding
Different thermocouples are color-coded according to their type. K Type thermocouples are color-coded Yellow.
K Type Thermocouple Monitoring
Thermocouples output a small voltage scale, which is converted using a formula to a temperature reading. The number of millivolts measured equates arithmetically to a specific temperature. K-type thermocouples have a good linear response. The graph below illustrates the different thermocouple types, their millivolt output, and equivalent temperature value for that reading.
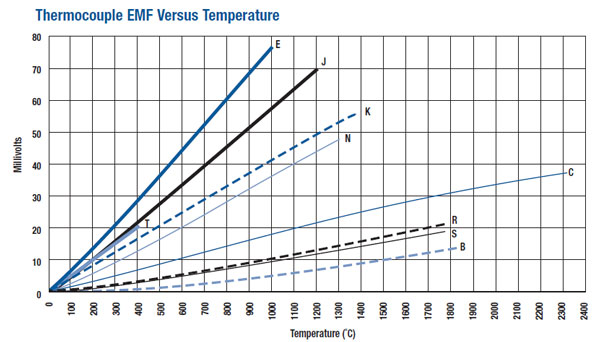
AKCP provides monitoring solutions for J and K-type thermocouples, allowing you to monitor the values online through the embedded web UI of the AKCP base unit. Alerts through SNMP, E-mail, and SMS messages are sent the specific temperature thresholds are exceeded. AKCP J and K type thermocouple adapters interface to any standard J or K type thermocouple. AKCP also supplies a complete package of adapters and thermocouples.


Summary
A K Type of thermocouples is inexpensive, small, dependable, and has fast reaction times. They can measure a wide range of temperatures from -270°C to 1,372°C with a small degree of error. Typically a K-type thermocouple is used in temperatures above 540°C and in oxidizing atmospheres.