The technology boom has had a massive impact on our daily lives. For much of our day to day life we now rely on the services data centers provide. Having a
backup plan in times of downtime is a top priority for data center owners and operators.
Modern organizations and businesses are heavily reliant on the use of data. It is a devastating event for many companies to loose data or have server downtime. One can only imagine how it would feel to have your server shut down due to technical failure.
This is one of the challenges for data centers. How does a data center keep its uptime at 100%? Here is where data center failover and redundancy come to play. Achieving minimal downtime and uptime tier certification is a guarantee of the data centers reliability.
Understanding Data Center Downtime

Photo Credit: cdn.buttercms.com
Every problem has its solution, and data center downtime is no exception. Failover and redundancy of systems is essential.
Downtimes can be painful to any business. The Information Technology Industry Council (ITIC) survey revealed that in 98% of organizations that suffered from an hour of downtime it cost them over $100,000. This news is further supported by a research report by the Ponemon Institute last 2016 that mentioned that the average data center outage cost was $740,357 USD, the highest being around $2.4 million USD. Those are quite big numbers.
Given these costs, it is critical to shed light on what causes downtime:
Power failures are often unpredictable. Typically, we only hear about it when it has already happened. Hence, it is essential that in cases like these, a backup system is implemented to prevent the loss of data.
It could be due to technical error or human error. Misconfigurations are held accountable for most network downtime cases. A redundancy model that makes such mistakes would not bring down the whole network.
-
Security Breach
Cyberattacks are relentless because they can breach even the best systems. In these cases, having a backup system is vital. Backups ensure that even if the primary systems are attacked, there are still others copies of data.
Sometimes, a network overload may take place. It is because of an incredible flow of internet traffic.
Due to data centers’ immense work, their components are prone to wear and tear. It makes the entire facility more vulnerable to malfunctioning.
In some cases, the presence of old files slows down the whole server, making it crash. This issue often takes a long time to address, ranging from a few hours to a couple of days.
In data centers, downtimes pose a massive risk to businesses and their profits. To prevent this, data centers use failover and redundancy systems to ensure a 100% runtime.
Datacenter Failover And Redundancy
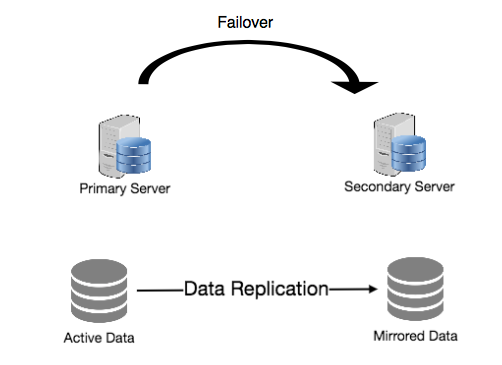
The big question then is what is data center failover and redundancy. Simply put, it is a system design wherein a data center’s components are duplicated in cases of emergency.
Data centers hold massive importance to many businesses worldwide. Because of this, data centers are meant to be resilient. They should be able to withstand disruptions as failure would cost companies much money. Thus, data center failover redundancy comes to play.
Failover is a backup system that functions when the primary components become unavailable. The failover system ensures that there is little to no server downtime in cases of emergency. It provides security so that no data loss takes place. It is like a power generator that automatically turns on when there is an electric shortage.
Redundancy, as the name may suggest, is the duplication of unit systems in a data center. It serves as a backup system in case one of the systems fails. Thus, when a system failure occurs, there is another system that serves as a backup. This backup would then have a duplicate copy of the data that should have been otherwise lost. A simple way to think of data center redundancy is a duplicate key. In buying a house, having a duplicate key is essential. It ensures that if anything happens to the original key, you will still be able to go inside your home.
Defining ‘N’ In Data Center Redundancy
Furthermore, there are different models of data center redundancy. All of these cater to a specific type of business niche. Before we delve into this, it is first essential to define the value ‘N’.
When we say ‘N,’ we refer to the least number of critical components needed for a data center to run at full capacity. It could refer to the number of units of cooling systems, UPS, or others that help keep the data center running. For example, if a data center requires at least four air conditioning units to run at its best, ‘N’ would be four. It happens because it is the least number of machines the data center needs to function.
The whole data center will risk losing the data if one of the units fails. Thus, there are different system models to prevent this from happening.
Data Center Failover And Redundancy Models

Photo Credit: medium.com
The data center has three main redundancy models, each of which is a more complex version of the other. These are the N+1 model, the 2N model, and the 2N+1 model.
The N+1 data center failure redundancy model is the simplest type of model. It means having an extra N component in case one of the components malfunctions. In an N+1 model, there would be a total of five air conditioning units. The additional unit is there in case one of the central units fails.
Design standards state that there should be one extra unit for every four units. Thus, if the data center houses 20 air conditioning units, it would need to have five backup units. These would then have a total of 25 air conditioning units.
Because of how straightforward the N+1 model is, it is often used by most businesses. It is cheap and more energy efficient when compared to others.
Next, we have the 2N model. If the N+1 model counterpart has a backup model for every four units, the 2N model is a complete copy of the original N unit. From the example earlier, this would give eight units of N for that data center. Hence, it is also known as the N+N redundancy model. With this, even if all the N units fail, the data center can still function optimally. It ultimately gives the data center incredible resiliency against adversities.
While the 2N model offers an excellent safety net, it is undoubtedly costly. Thus, the 2N model is usually best for businesses that need a more sophisticated system. Examples are hospitals and financial institutes.
Lastly, there is the 2N+1 redundancy model. As the name suggests, it is the combination of the previous models of data center redundancy. It is the most expensive, albeit the most secure, out of all the discussed models. The 2N+1 is usually used by corporations that cannot have any form of inconvenience.
Optimized Data Center With AKCP Monitoring Solutions

Wireless Thermal Maps
AKCP offers a wide range of monitoring solutions for your data center. While data centers can cut the risk of downtimes by overcooling, they waste so much energy. If left unattended, overheating can happen. We can provide a solution that ensures you get the best of both worlds. AKCP’s Thermal Map Sensors and AKCPro Server Heatmaps ensure that the data center runs well.
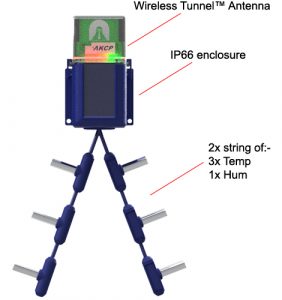
Featuring six temperature sensors and two humidity sensors, AKCP Thermal Map Sensors can provide your data center with real-time heat maps at the rack level. Combine this with AKCPro Server Heatmap, hotspots are then identified, and alarms are raised, ensuring that problems are prevented.
When the primary power source fails, an uninterruptible power supply ensures that the network systems continue to function. As a result, the business runs the danger of having downtime for its data center,
server room, and other critical equipment if it is not adequately monitored. These mistakes may even have negative effects on service quality, clientele loss, and financial loss.
AKCP Power Monitoring Solution monitors the different metrics of UPS devices including bypass mode, changeover, power, remaining battery, battery mode, frequency, ambient temperature, and more. With a monitoring system in place, you will be able to check the current performance of your UPS and send you alerts on critical.
AKCPro Server provides a UPS monitoring system that can monitor and send customized alerts via SMS and email in real-time and remotely.
Features:
Remaining Battery

Power Monitoring Sensor
Measures the remaining battery of the UPS and immediately alerts the users once the battery reaches a critical level.
Ambient Temperature
Monitors the temperature of the UPS and alerts once it detects abnormality with the temperature level. Maintained temperature helps increase the battery life.
Power
Monitors the power from the UPS.
We offer both conventional wired and wireless data center monitoring systems. Based on LoRa technology, our Wireless Tunnel System has features tailored to the requirements of data center monitoring. Wireless sensors provide rapid deployment, simple installation, and a high level of security. It is the only LoRa-based radio solution with instant notifications and on-sensor threshold level checks that has been created only for monitoring critical infrastructure.
Conclusion
As we increase our reliance on technology, the way businesses work has also changed. Data and information are now the backbones of many companies. Even a short downtime can cause severe consequences to them. The challenge for data centers is to ensure they keep a 100% uptime of their services.
Data centers use failover and redundancy strategies to keep themselves running despite emergencies. These strategies include N+1, 2N, and 2N+1 models.
References
https://www.evoquedcs.com/blog/data-center-redundancy-explained
https://www.coresite.com/blog/data-center-redundancy-n-1-vs-2n-1
https://www.digitalrealty.com/blog/2n-vs-n-1
https://axi-international.com/data-center-redundancy-and-tier-classifications/
https://www.akcp.com/blog/data-center-redundancy-and-tier-classification-levels/