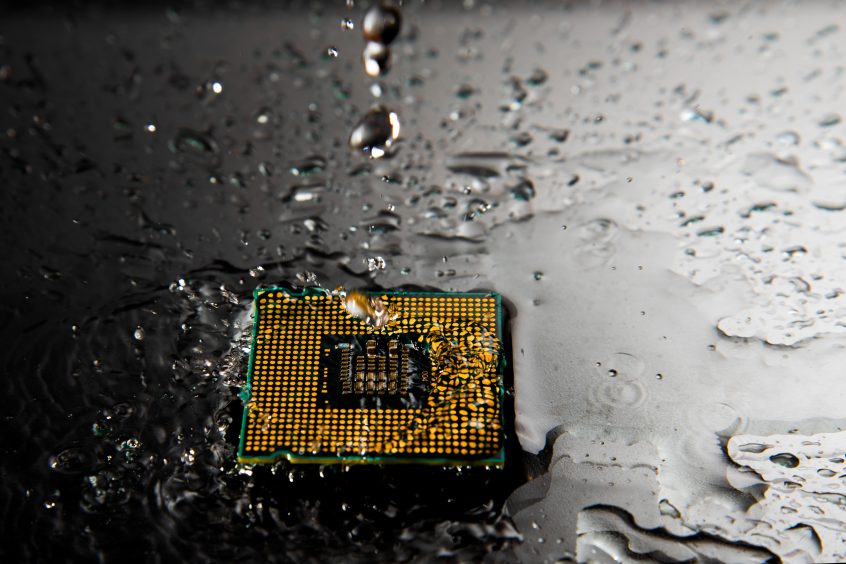
Data centers are undergoing significant transformations as large artificial intelligence applications become more common. To meet the demands of high-density IT infrastructure, data centers are adopting innovative solutions, and one such technology is data center liquid cooling. This article explores the evolution of data center cooling, the advantages of liquid cooling, and its use cases across various industries.
Efficiency and Data Center Cooling:
Efficiency remains a key factor in managing data centers, ensuring maximum uptime while reducing operational costs. Identifying efficiency loopholes is crucial, especially as the IT infrastructure grows larger. New technologies are being introduced to stay ahead of the curve, and data center administrators are recognizing the importance of optimizing cooling systems to meet high-density demands.
The Road to Liquid Cooling
Data center cooling has evolved over the years, with efforts focused on enhancing efficiency and uptime. One popular technology is liquid cooling, which has evolved from a concept to a proven case study. Liquid cooling studies serve as fundamental references for implementing proper cooling practices.
Advancements in Data Center Cooling:
In the mid-1990s, hot and cold aisle organizations were introduced as a way to optimize server rack arrangements. In 2005, server cabinets with vertical exhausts demonstrated significant reductions in cooling energy costs. By 2006, data center airflow management shifted towards efficiency, leading to measurable energy savings. Over the years, air cooling technologies remained the standard, but they are starting to face limitations in supporting next-generation IT infrastructure.
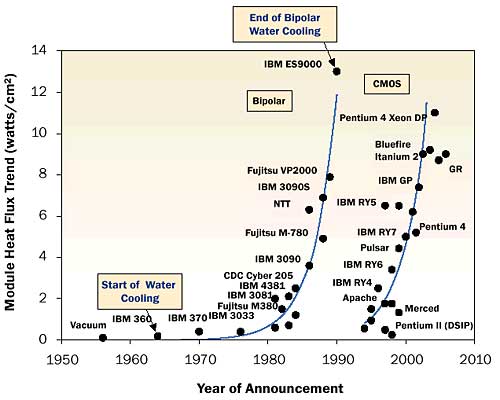
Photo Credit: electronics-cooling.com
In 2010 ASHRAE published documents focusing on the economization of cooling energy, ASHRAE 90.1 or the Energy Standard for Buildings. Additional stipulations include variable fan flow and humidity management. These became the reference for the new way of data center management.
From the 1990s to the mid-2000s, air cooling technologies were still the go-to option in data centers. For the longest time, raised floor systems have facilitated cold air movement to IT servers. Cooling the data center by cooling the air is still the standard solution up to this day.
The more significant issue to address is how air cooling can keep pace with next-generation IT infrastructure? Can an air-conditioned unit sustain hardware reliability? Can it maintain the correct temperature conditions for computer rooms? Air cooling is starting to reach it’s limitation and new technologies needed to be explored.
The Advent of Liquid Cooling
The necessity of removing heat from data centers is an ongoing concern to prevent equipment damage and downtime. Traditional air cooling has its downsides, such as particle and gas contamination, which can shorten equipment lifespan. Liquid cooling emerges as a direct alternative, offering higher efficiency levels, scalability, and optimization of server workload delivery.
Liquid Cooling Use Cases

Liquid cooling technology finds applications in various industries:
- Artificial Intelligence: To support high-density IT ecosystems necessary for AI and machine learning, liquid cooling efficiently removes heat from a large cluster of IT hardware, surpassing traditional cooling options.
- Smart City: Liquid cooling enables integrated technology support in smart cities, maintaining service levels and tech reliability.
- Oil and Gas: Remote data centers with liquid cooling provide uninterrupted uptime for the critical trade and commerce involved in the oil and gas industry.
- Financial Services: Liquid cooling becomes a crucial part of data center planning for banks and financial institutions, ensuring fast and reliable computing for instant money transfers.
- Gaming: With the rapid growth of the entertainment and e-sports industries, liquid cooling solutions are essential to meet the high-density technology demands.
- Education and Research: Liquid cooling helps support new educational platforms and research ventures that require significant computing power.
Monitoring Your Data Center
To protect and maintain data centers with high-performance demands, comprehensive data center monitoring is essential. AKCP data center monitoring sensors offer monitoring solutions for power efficiency, temperature, humidity, water, and more. These sensors help prevent IT failures and downtime by providing timely alerts.
AKCP data center monitoring sensors provide a comprehensive monitoring solution for these parameters. AKCP sensor solutions functions include:
- Monitor power efficiency with live PUE readings.
- Comply with ASHRAE standards for temperature in cabinets.
- Access control and security for cabinets and doors.
- Integration to third-party equipment.
- DCIM software for user access.
- Prompt notification to alert from disaster before it happens.
Data Center Liquid Cooling Considerations
Data centers are evolving rapidly, and liquid cooling technologies are playing a vital role in meeting the demands of high-density IT infrastructure. As various industries rely heavily on data centers, the implementation of liquid cooling solutions becomes increasingly necessary to ensure efficiency, reliability, and cost-effectiveness. With advancements in technology, liquid cooling has emerged as the most logical and effective solution for removing heat and sustaining the performance of modern data centers.
Reference Links:
https://datacenterfrontier.com/the-evolution-and-the-adoption-of-liquid-cooling-for-data-centers/
https://www.avnet.com/wps/portal/integrated/resources/article/liquid-cooling/






