The data center is a high-risk environment that necessitates the use of qualified staff. It’s a good idea to have a data center safety plan. However, if it is not effectively applied, it will be useless. As a result, an unskilled or inadequately trained engineer is kryptonite for data center safety. Safety culture is only as strong as its weakest link.
Risk assessment, equipment-specific lockout/tag-out procedures, electrical work, working at heights, hot work, lifting and handling, sensor technology and digitalization, and contractor management are the eight categories. These components are the key areas when it comes to data center safety.
The following is an efficient and wise approach to data center safety guidelines:
- Investigate and identify potential dangers.
- Systems, policies, processes, and procedures should all be audited.
- Improve the situation.
We’ve prepared a checklist below that outlines how to accomplish so using eight major focus areas. We’ll also discuss social distance and other safety-related aspects of the global data center epidemic, as well as how to respond accordingly.
Conduct A Comprehensive Risk Assessment

Photo Credit: actnowtraining.files.wordpress.com
Perform a standard data center safety risk assessment to check all of the following before starting any job:
- Identify the risks and hazards of the job.
- Eliminate or mitigate the risks by implementing controls.
- Obtain the appropriate permits.
- Follow all safety policies and procedures.
- Use proper personal protective equipment (PPE).
- Training, training, and more training.
If a worker discovers any safety gaps before beginning a job, they must reduce or eradicate those gaps before proceeding. It’s a cliche, but workers must view it through the lens of the continuous improvement cycle. It must be in the action plan, and it must be active and strive to ensure a safe working environment.
Review Equipment-Specific Lockout/Tagout Procedures
The establishment of an energy control program that ensures employee safety is required for proper lockout and tag-out processes. Equipment must be locked out or tagged out while in use, or conform with further energy management provisions in OSHA standards when permitted. More information from OSHA can be found here.
- Bring staff up to speed on the lockout/tag-out choices for every piece of equipment they manage, and instruct them on how to use them.
- Many firms only provide basic annual lockout/tag-out training, which may meet OSHA requirements, but if you want to establish a safety culture or take your safety program to the next level, detailed and equipment-specific lockout/tag-out training is the best way to go.
Supervise Electrical Work
Electrical work guidelines are similar to lockout/ tag-out guidelines. Before providing IT equipment access, make sure everyone is properly trained.
- Identify all known electrical hazards.
- Make a list of all known electrical dangers.
- Meet or exceed the requirements for competent workers.
- Establish a guideline for minimizing energized electrical work.
- Employees should be trained on specific electrical equipment and processes.
Prep For Working at Height
Accidental falls and dropped objects can have disastrous consequences for data center engineers and the IT equipment they are working with. Ascertain that workers are capable of working at any height.
- Create particular protocols and training for working at heights on ladders and roofs, as well as employing cranes, lifts, and scaffolds.
- Regularly inspect and test work-at-height equipment for standard safety inspections.
Avoid Hot Work

Photo Credit: www.powerandcables.com
Any work involving combustible, ignitable, or flammable materials falls under this category. If you have to undertake some hot job, you should:
- Determine where welding and cutting will take place in defined “safe zones.”
- Before starting work, some organizations prohibit hot work near IT infrastructure and relocate hazardous goods.
Enforce Safe Lifting And Handling
Sticking to the 50-pound manual lifting limit and providing personnel with the right gear for lifting bigger servers and other hardware is the best approach to creating an effective lifting and handling safety strategy.
- Manually lifting anything weighing more than 50 pounds is not recommended.
- If an object weighing less than 50 pounds needs to be moved, make sure personnel are trained in situational awareness and know when to use a data center lift.
- Teach proper lifting skills to people who use assistive equipment and those who don’t.
- When mechanized lifting systems are required, use them.
Embrace Sensor Technology And Digitalization
A wide range of sensors including temperature, humidity, airflow, motion detectors, etc… can be connected to the sensorProbe and securityProbe units.
According to Leclerc, creating a smart, responsive data center is the way of the future: “It’s about offering operators real-time information to understand their work environment.” Human error is also reduced, and data centers may function with fewer employees.
The following technologies are being developed or already exist:
- Noise levels can be monitored in real-time from afar. Employees can determine whether a generator room exceeds recommended decibel levels before entering.
- In the absence of voltage testers (AVT), keep an eye on electrified systems.
- Digitally monitor water usage using ultrasonic flowmeters.
- Predictive analytics is being used by certain firms to prevent injuries and reduce unplanned downtime of IT equipment.
- In addition, new technology is emerging across industries that use remote monitoring sensors (RMS) to check AEDs for constant functionality issues, removing the need for onsite monthly inspections.
Contractor Management
Any data center operator who hires vendors or contractors must ensure that the employees they hire are qualified for the job. Before permitting service providers on the data center floor, data centers should require them to complete systematic safety training.
- Match your data center’s safety policies to those of your vendors and service providers.
- Throughout your facility, post clear and visible safety signage.
Data Center Safety Protocols Shifting With The Pandemic
While social distance and COVID-19 are top of mind, Leclerc believes that they do not alter proper safety practices in any way. Because the data center is a naturally controlled setting, we have social distancing built-in.
In a well-prepared data center environment that equips staff with the proper tools, social distancing develops organically. When dealing with any of these problems, and an empowered worker will be the safest and most productive.
Keep The Employees’ Safety With AKCP Wireless Sensors
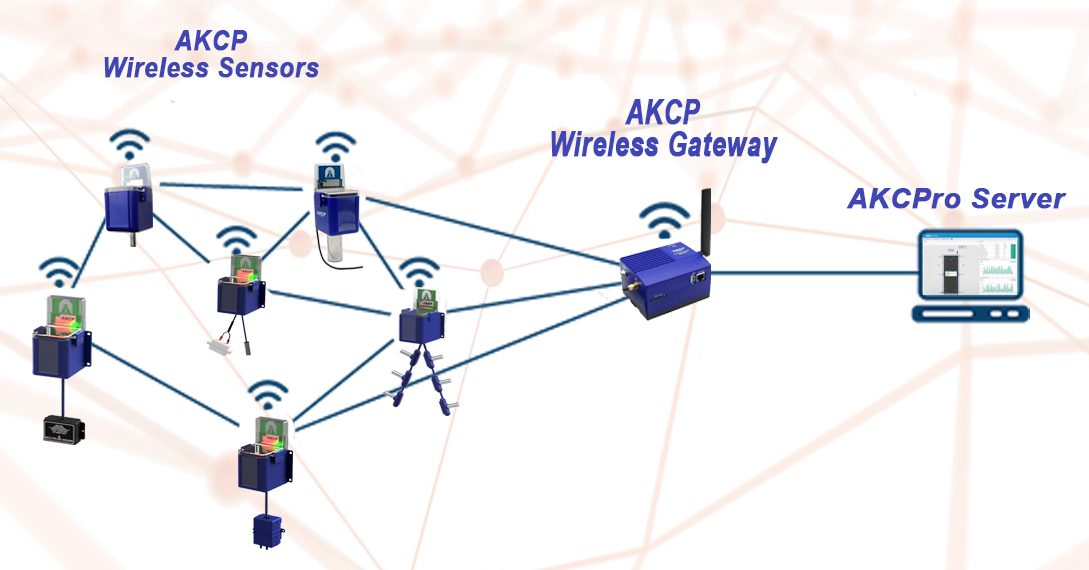
AKCP Wireless Sensor Network
AKCP Data Center Wireless Sensors
There is a wide range of wireless environmental sensors on the market. Typically they are not targeted for use in data center or server room monitoring. AKCP has over 30 years of experience in providing professional sensor solutions for the data center. They took on the challenge of developing wireless environmental sensors that were tailored specifically for monitoring critical infrastructure. They have brought to market the world’s first LoRa based monitoring system with features specifically for the data center. The Wireless Tunnel is a holistic approach to wireless sensor monitoring. It comprises:
- Wireless Tunnel Sensors
- Wireless Tunnel Gateway-Server
- AKCPro Server
Wireless Environmental Sensors
AKCP created the market for environmental monitoring in the data center. They have a wide range of environmental sensors that cover the needs of large data centers down to small in-house server rooms.
Cabinet Thermal Maps give temperature and humidity values for the front and rear, top-middle-bottom of the server cabinet as well as the front to rear differential temperature readings (ΔT).
The Cabinet Analysis Sensor combines cabinet thermal maps with front & rear differential air pressure (ΔP), suitable for data centers using hot and cold aisle containment. All of these environmental sensors and more are available as part of the Wireless Tunnel system.
Wireless Tunnel Gateway-Server
The sensors require a gateway to communicate with. The Wireless Tunnel Gateway Server collects and stores data from up to 30 environmental Sensors. In small installations, the Gateway-Server is used as a standalone monitoring system without the need for a cloud server or internet connection. The embedded user interface of the server provides customizable desktops, mapping, and graphing. Alerts are sent via SMS, E-mail, and SNMP Traps. All of the features found in the AKCP sensorProbeX+ user interface are available on the Gateway-Server. These include
- Up to 80x virtual sensors
- SNMPV3
- RADIUS
- VPN
- IPV6
- Tunneling Cloud Service
Wireless Tunnel Server
For larger installations with multiple gateways, a centralized monitoring platform is used to combine the data from all gateways. The Wireless Tunnel Server is a central management platform, AKCPro Server. The server software can be run in-house on your own server or hosted in the cloud. It is a Data Center Infrastructure Management (DCIM) platform with close integration to AKCP environmental sensors
Reference Links:
https://www.datacenterknowledge.com/industry-perspectives/six-golden-safety-rules-data-centers
https://www.techtarget.com/searchdatacenter/tip/Best-practices-for-data-center-risk-assessment
https://www.safetysure.com.au/safety-advice/managing-work-health-safety-in-a-data-centre/





