As many businesses are under pressure to speed digital transformation, IT professionals are striving to integrate cloud and data center colocation solutions to enhance the efficiency of their current infrastructure. When weighing the advantages of colocation versus cloud, it’s evident that the two aren’t mutually exclusive, with many businesses opting for a hybrid solution that best suits their needs. A blend of colocation and cloud could be very useful for balancing requirements like security, flexible compute resources, and legacy applications.
What Is Colocation?
Many people believe that colocation is simply a data center where you can rent space, obtain electricity, and connect to the Internet. Colocation, on the other hand, is about more than just data center space.
Today’s colocation data centers provide a variety of services, ranging from managed IT to hybrid cloud. They can also give you more power density, which is important for scaling and supporting new technologies quickly. Some data center colocation providers also provide direct access to popular public cloud platforms like Google Cloud Platform, Amazon Web Services (AWS), and Microsoft Azure.
Traditional Colocation Models
When you look for a data center colocation provider, you’ll find the following traditional colocation models:
- Wholesale
In this model, you lease data center space that is customized to meet your needs. This model is best if you have large power requirements and need more than 10,000 square feet of space.
- Retail
In a retail model, you lease space inside a cage. Consider this option if you don’t require a lot of power and can fit your equipment into less than 2,500 square feet of space.
Whichever model you choose, look for a data center solutions provider who offers more than just the basics. Find a partner who understands your business, can meet your power requirements, can help you quickly scale, and can possibly help you with a Retail+ model that bridges the gap between wholesale and retail.
What Is The Cloud?

Photo Credit: www.rahisystems.com
The term cloud means different things to different individuals.
Some people associate a cloud with virtualization or a public cloud. Others define it as containers or a private cloud. A hybrid cloud, according to some, is one that blends public and private resources. For many, the cloud represents a commercial risk.
With so many definitions, it’s crucial to define cloud within your company, get everyone on board, and understand the financial ramifications.
Cloud Defined
“A model for enabling ubiquitous, convenient, on-demand network access to a shared pool of configurable computing resources that can be rapidly provisioned and released with minimal management effort or service provider interaction,” according to the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST).
According to NIST, the cloud has the following five characteristics:
- On-demand
- Broad network access
- Resource pooling
- Rapid elasticity
- Measured
What Is Managed Cloud?
Most public cloud providers, such as AWS, provide services that meet the NIST definition of cloud, but they don’t manage your workloads or provide an interface to your existing IT systems.
The benefits of the cloud are combined with full-service operational management of the workloads hosted there in the managed cloud. Managed cloud providers are concerned with your complete IT service framework.
The Difference Between Cloud and Colocation
Photo Credit: www.aixit.com
Colocation is where you provide the equipment, and the colocation provider hosts it in their data center and provides the space, power, rack, and bandwidth. The cloud is not a place, rather software and hardware are available via the Internet.
Smaller operations and startups usually opt for the cloud because of the scalable cost, low overhead, and no need for an IT staff. Larger enterprises often go the colocation route to house their servers because it saves money in the long run, and it offers the benefit and flexibility that comes with total server control.
Types Of Cloud
- Public Cloud
This is a type of infrastructure that has a big number of servers and is used by a variety of companies. These are cloud service providers’ Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS) and Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS) solutions. In many cases, such as with HostDime cloud, the client pays only for the CPU, RAM, and disk space that they use.
- Private Cloud
This is infrastructure in a data center, on-site or off-site, that is dedicated to your data and is tailored to your requirements. This private network is just for the use of your company. Colocation is a type of private cloud in which an organization buys its own servers and equipment and stores it in its own rack space in a data center.
- Hybrid Cloud
This is when public and private cloud environments coexist. Hybrid cloud computing mixes on-premises or colocation servers with public clouds, allowing data and applications to flow between the two for enhanced agility, security, and cost-effectiveness.
Similarities Of Colocation and Cloud
Cloud and colocation both save businesses money, with cloud providers providing virtualized shared public resources. The resources within racks and cages are not shared; they are dedicated to the firm that owns them. Colocation is shared space within a data center, but the resources within racks and cages are not shared. In a colocation facility, shared resources include:
- Redundancies and cooling systems
- Redundancy and power systems
- System of security
Colocation Costs Vs Cloud Costs
Colocation services have higher upfront costs as compared to cloud-based options. This is because, rather than transferring data to a cloud provider’s servers, users must purchase their own gear. On the other hand, the pricing structure of cloud hosting services will frequently tilt the balance back toward colocation. Despite the fact that cloud services are scalable and offer a lot of power and flexibility, getting access to them can quickly become prohibitively expensive.
Colocation, on the other hand, necessitates the ongoing maintenance and replacement of equipment. The supplier uses a cloud-based method to perform all updates. Even if a firm isn’t ready to think about how it will manage its IT infrastructure’s server refresh cycle, the cloud may be a more convenient, albeit not always more cost-effective, option.
Colocation + Cloud = Enhanced Agility at Lower Costs

Photo Credit: www.tallerdeempresa.com
A data center requires both financial and technological resources to construct. Even small data center facilities start at 10,000 square feet, implying that even a small data center may cost $2 million or more to build. Most firms can’t afford new IT equipment, let alone the funds to update or build a new structure.
Because data center investment and reinvestment are difficult to predict, companies are looking for more predictable and accurate techniques to manage their infrastructure technology cost. By migrating to the cloud and colocation, businesses can move away from the CAPEX roller coaster and toward a more linear operating expenditures (OPEX) financial model.
When you combine colocation and the cloud, you can manage your workloads without the exorbitant costs of owning your own data center. This frees up resources to focus on innovation and growth rather than basic infrastructure and operations.
Low-latency connectivity in a convenient location has been made possible by a collaboration between colocation and cloud providers. This enables you to quickly scale, build apps, and meet new business demands.
Colocation also offers benefits that the cloud alone does not. Compliance, for example, is difficult to maintain on the cloud. Many colocation providers meet high compliance and security criteria to give you secure access to the cloud.
To get the most out of the cloud, look for a colocation provider that offers managed services, managed hosting, and migration services. By outsourcing your day-to-day IT operations to your data center solutions provider, you may save money and free up your internal team to focus on innovation. Your colocation supplier should supply skills that you don’t have in-house, whether it’s managing outdated equipment when key personnel departs or utilizing new technologies that you can’t handle in-house.
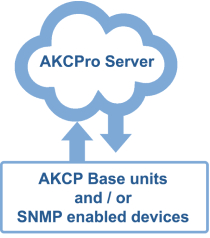
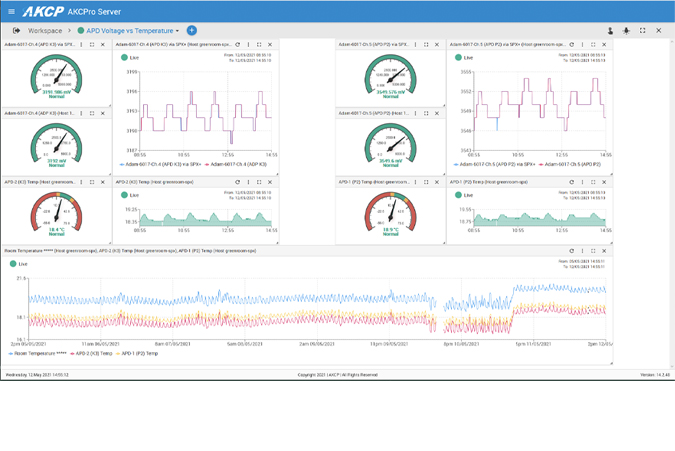
AKCPro Server
Central Monitoring Software
AKCP Cloud Monitoring
Monitor All Your Base Units
If you have several base units deployed within your building, or over a large area, add each device to your AKCPro Cloud Server and log in anytime to see all your sensors organized as you wish on custom desktops. Multiple logins can be used for different users who need to see different data. Display sensors on drill-down maps.
Alerts In The Cloud
E-mail, SNMP Trap, SMS, and phone-call notifications are all available in AKCess Pro Cloud Server. Configure e-mails yourself, or use our e-mail service to send unlimited e-mail alerts. SMS and Phone call notifications can be sent for a fixed-rate annual fee. Know the moment your sensors are in critical condition.
cloud monitoring plays a crucial role, enabling the provision of a shared set of technological services to companies, allowing access from anywhere in the world and on-demand to a shared set of computing resources.
Reference Links:
https://searchservervirtualization.techtarget.com/tip/What-is-the-difference-between-private-cloud-vs-colocation
https://www.vxchnge.com/blog/colocation-vs-cloud
https://phoenixnap.com/blog/colocation-vs-cloud
https://www.deft.com/blog/its-not-colocation-vs-cloud/