An uninterrupted Power Supply (UPS) is one of the most essential components of a data center power train. UPS serves as a barrier for the most critical IT equipment. It provides electricity and power backup to load whenever it is needed.
UPS also protects IT equipment from power impurities. The electricity that comes from the grid contains pollutants which include harmonics, over-voltage, sag, spike, and swell. Datacenter servers are highly sensitive to these fluctuations. If the IT load is subjected to raw power supply, servers are highly vulnerable to failure. Servers may also get burned due to high voltages.
Hence a UPS is critical to the overall operation of data centers. However, UPS is also prone to failure. This system can fail even when utility power is stable. Random UPS failures like this can be solved easily with automatic bypass mechanisms. A remote or local alert system tells you if there is any immediate action needed.
But a UPS failure related to utility power failure can be tough. This type of failure leads to unplanned downtime. Today, we look at the common causes of UPS failure in data centers. What to know about it – and what you can do about it.
Understanding UPS Systems in Data Centers

Photo Credit: serverroomenvironments.co.uk
Before knowing UPS failures, you need to understand UPS systems first. UPS stands for uninterruptible power supply. As mentioned, it is a device that provides a backup supply of electricity. It also regulates the electricity that powers critical IT equipment.
UPS systems have energy storage batteries. It connects short-term power loss between utility power failure and backup generator systems. UPS systems typically function for up to 10 minutes or more. Just long enough toast until the generator takes over.
-
Components of UPS Systems
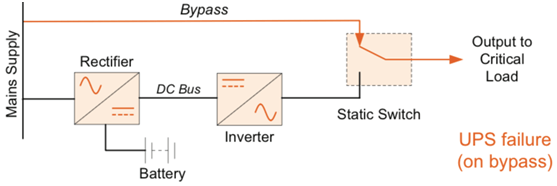
Photo Credit: www.kohler-ups.co.uk
-
- Rectifier
It receives AC power from an input source. The AC power is then converted to DC power to provide energy to the inverter. As well as charge the battery bank or energy storage.
-
- Battery bank or Energy Storage
All UPS have some kind of system to store electricity. This electricity can be stored in the form of batteries, flywheels, or supercapacitors. This makes UPS supply uninterrupted power. In online UPS, nickel-cadmium or free lead-acid batteries are typically used.
-
- Static Bypass
Also known as automatic bypass. In case of UPS failure, the input power source delivers static bypass without break.
-
- Manual Bypass
Also known as maintenance bypass. This is utilized when UPS systems need maintenance.
-
- Inverter
It converts DC power from the rectifier into AC power required by the load. It delivers the required voltage and frequency in the outputs of UPS.
Common Causes of UPS Failure

Photo Credit: Gadget Addict YouTube Channel
UPS failure is a leading cause of unplanned power outages in data centers. It results in costly downtime service and disrupts the overall operation of data centers. Batteries are the major culprit of UPS failure. Every UPS system has a set of batteries. One battery failure can lead to the failure of the entire set. Essentially, without the batteries, the UPS system cannot function.
Fans also play a major role in UPS failure. Most UPS systems have several fans. If these fans do not function properly, the system will overheat and shut down. Typically, fans can last for seven to 10 years. It depends on how frequently they are used. It can also vary with the temperature that fans work with. Note that the temperature they work with should be around 22°C to 25°C (72°F to 77°F).
Capacitors are also essential to the operation of UPS. They filter out the voltage spikes. If capacitors fail, the UPS system will not function. Typically, these components also last for seven to 10 years. Just like the fans, they also depend on the temperature they work with. If the temperature is higher, the capacitors will likely shrink immediately.
Here are a few more causes of UPS failure.
- UPS Ran-Out of Power
UPS failure is sometimes caused by power outages that last longer than the battery of UPS.
- Unmaintained and Unmonitored UPS
It can be that the old batteries were not replaced when the power outage occurred. Hence, the UPS system does not have enough stored electricity to continue operating.
- Blown Fuses
Sometimes the UPS is placed incorrectly into the bypass. As a result, the fuses are blown. The rectifier fuses or inverter fuses can also be blown.
- Overloading or Underloading
Overloading happens when the grid power requires more electricity than the UPS system could provide. This leads to the internal bypass of UPS. Meanwhile, underloading occurs when the power supply given to UPS is less than the power supply it needs.
- Capacitor Failure
AC power and DC power capacitors must be replaced regularly. The rule of thumb according to manufacturers is to replace capacitors every five to seven years.
- Dust Builds-Up
The built-up pollutants inside the UPS can cause components to overheat.
- Fans may not be Operating
This can lead to the system overheating and shutting down.
- Outdated UPS System
Like any other device, a worn-out and old UPS system cannot function efficiently. Overused UPS systems can lead to the failure of electrical components.
Prevent UPS Failure
Sometimes UPS systems automatically change to on-bypass alerts. This is typically caused by external or internal issues or no reason at all. Due to this, on-bypass alerts are usually neglected. But this should not be the case for the operators. In this mode, the UPS fails to secure IT equipment against utility power failures. The backup power is not operational. Hence, it is essential to monitor the working model of UPS. Do the necessary adjustments to put UPS into its necessary working mode.
Look out for the batteries. Failed or weak batteries also need immediate action. A battery set that operates at eight minutes may function less over time. Working only for five to six minutes. Sometimes it may not function at all without any warning.
Failures of lead-acid batteries are a major cause of UPS failure. UPS batteries should always be monitored even if they are relatively new. Batteries should be tested at least every year. If the batteries are not monitored properly, they may end up not functioning at all.
Monitor the air filters as well. Dirty air filters can lead to overheating and weakening of internal UPS components. So be sure to clean air filters in the facility.
Make sure that you maintain the right temperature in the storage of UPS systems and batteries. High room temperatures can lead to cooling failures. As well as overheating of UPS systems and equipment downtime.
Prevent UPS Failure with AKCP

AKCP Battery Monitoring Sensor
Monitoring is one of the best measures to prevent USP failure. For your data center monitoring needs, visit akcp.com. AKCP was established in the USA in 1981. With more than 30 years of experience in professional sensor solutions. AKCP created the market for various monitoring solutions in data centers. Today, AKCP is the world’s oldest and largest manufacturer of sensor solutions.
Battery Monitoring Sensor
Monitoring the voltage, temperature, and current load for batteries and DC power systems. The Battery Sensor monitors an individual cell or bank of batteries. As well as DC power systems like solar panel arrays. With this sensor, you can monitor:
- The temperature of the battery terminals
- The voltage output from batteries or panel array
- Current load on batteries or charging circuit
Wireless Battery and Solar Panel Sensor
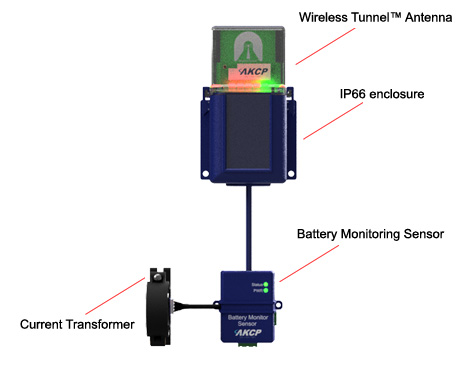
Wireless Battery and Solar Monitoring
Wireless Tunnel™ radio module with battery monitoring sensor can check battery health and solar panel output. And check solar panel efficiency. Monitoring current draw of batteries to ensure charging current is sufficient. The sensor monitors Voltage, Current, and Temperature. Works with all Wireless Tunnel™ Gateway.
Sensor Details
- 4x AA Batteries
- External 5VDC or 12VDC power
- LED indicators for power, status, and RSSI
- Optional DIN rail or pipe mounting
Typical applications would be for monitoring a battery bank, solar panel array, or generator starter batteries. Visit akcp.com for more details.
Power Monitoring Sensor

The AKCP Power Monitor Sensor gives vital information and allows you to remotely monitor power. Eliminating the need for manual power audits. As well as providing immediate alerts to potential problems. The AKCP Power Monitor Sensor is specifically designed to be used with AKCP sensorProbe+ and securityProbe base units.
It has been integrated into the sensorProbe+ and securityProbe web interface with its own “Power Management” menu. Allowing multiple three-phase and single-phase Power Monitor Sensors to be set up on a single sensorProbe+ or securityProbe. Depending on which readings are required. Visit akcp.com for more details.
Conclusion
Electricity is the ultimate fuel of data centers. Like any modern industry, data centers operate with a power supply. A secure power supply is essential to every IT facility. Power interruptions can have a significant impact on the operations of a data center. It can damage the most delicate IT equipment, leading to costly downtime. Backup supply then is vital to secure and prevent damages to IT facilities.
UPS failure has a significant impact on the functions of the data center. That is why it is important to monitor the different components of UPS systems. Note that the batteries are the most important component of UPS. When the batteries malfunction, the whole system cannot operate. Always monitor the room temperature where the UPS system is located. Do not forget the regular maintenance and monitor on all parts of UPS to prevent failure.
Reference Links:
https://www.facilitiesnet.com/datacenters/article/5-Areas-of-UPS-Failure-to-Look-Out-For–18999
https://www.datacenter-serverroom.com/server-room/how-ups-for-server-room–data-center-works
https://www.pcmag.com/encyclopedia/term/ups
https://www.allaboutcircuits.com/technical-articles/uninterruptible-power-supply-systems-in-critical-data-centers
https://powercontinuity.co.uk/knowledge-base/ups-failure-common-causes/
https://weisscopower.com/most-common-causes-of-ups-failures/