Airflow management is vital for a data center’s success. Ensuring that layout facilitates better airflow are primary routes to better IT operation. The rise of high-density data centers is the renewed hurdle for IT managers to improve airflow.
One of the primary considerations in airflow management is bypass airflow. Reducing the occurrence of bypass airflow will have a significant benefit in one’s IT operation. The risk involved in negating the better airflow passage will be detrimental in the long run. Hence, determining some steps to eliminate the risk is the best solution.
Bypass Airflow And Its Significance To Data Centers
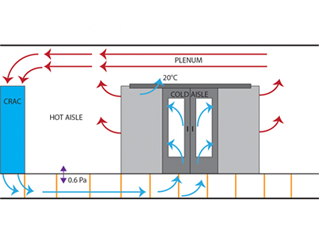
Bypass refers to the quality air that goes past or around its intended route. In theory, cooled air will pass from the CRAC through the server and nowhere else. This is not the case for bypass airflow. Bypass air finds a route back to the CRAC air intake without passing through the IT equipment. This, therefore, means it is wasted cooling energy.
How Does This Affect The Whole Data Center? How Significant It Is To Regulate Bypass Airflow?
The main reason why air does not flow as intended in an IT room is an opening that circumvents the proper airflow. Unmanaged spaces will elicit more options for air to pass through. This rescinds the regular airflow pattern in the process.
Some examples of bypass openings are as follows:
- Perforated tiles (tiles with punctures or holes in raised floors)
- Cable openings
- Open spaces in server panels
The main concern from this airflow issue is it increases the unconsumed volume of air by the IT equipment. Such conditions mean that IT hardware does not fully utilize the cooling capacity of the air because it bypassed the equipment.
When this happens, cooling capacity is underutilized. More bypass air in the server racks will mean lesser cooling. Ultimately, it could mean that when servers are under increased load they get insufficient cooling. Or, your cooling capacity is over specified to compensate for the losses through bypass airflow.
Misconceptions On Bypass Air Management
Air takes up space and has mass. Air has complicated properties to manage. The misunderstanding stems from not recognizing its properties.
Reducing bypass airflow, for that matter, is not confined to sealing holes and openings alone. Some traditional data centers rely on sealing cable openings to manage the problem. It is much complex than it may seem.
Covering intentional openings alone will facilitate a new stream for bypass air. When data centers have running cooling strategies, sealing such gaps will only shift bypass airflow. Worst it may take up space along the cold aisles.
Some IT rooms implement many ways to counter the effect of bypass airflow. These are practices to change the cooling capacity limiting the impact of bypass airflow. Some of the best practices are:
- Improvement of intake air temperatures for IT
- Improvement of equipment reliability
- The heightened volume of cooling airflow specifically projected to perforated tiles
- Cooling of cabinets without raising floor static pressure
Improving Bypass Airflow
A vital precursor to any improvement activity is taking in the root of the problem. It is only in understanding the sources of bypass airflow will IT managers can address the issue. Some basic steps will aid in curbing the harmful effects of bypass airflow:
-
Measure A Data Center’s CCF
The existing Cooling Capacity Factor (CCF) is a vital indicator to come up with improvement remedies. Do note, however, that CCF is influenced by many factors such as:
- Cooling unit size
- Cooling unit number and location
- Room layout
- Heat load distribution
- Height of raised floors
- Ceiling height
But these are complex attributes that will harden the whole improvement plan. To simplify all that, CCF can be calculated as:

Photo credit: www.upsite.com
Knowing the data center’s CCF is critical in your subsequent steps for airflow improvement.
-
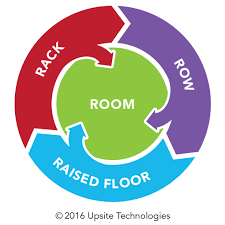
Make Improvements For 3 R’s

Photo Credit: gstatic.com
There are essential features of data centers that are integral in the whole airflow management. These are: (1) Raised floor, (2) Rack, (3) Row. To do these, here are some basic steps to follow:
- Specifically, control the airflow in the open area of the raised floor. To achieve this, sealing cable openings is a must. There must be a check for any case of perforated tiles as well. Inspect the perimeter of the raised floors. Shutting any partition or openings will be helpful.
- Inspect the IT equipment intake. Specifically cover the open spaces situated in the vertical plane. Installation of blanking panels, cabinet seals, rails, and side seals are also a primary task to oversee.
- Organize the alignment of IT equipment cabinets. Open spaces and gaps are a no-no. For higher density, IT infrastructure, hot or cold aisle may be more applicable.
-
Determine Cooling Set-Up
The fundamental consideration for a cooling infrastructure is to sustain temperature at specific set points. As such, the particular checkpoint must include:
- Selection of cooling unit that is capable of raising the air temperature. Raising temperature parameters is critical. The cooling unit should achieve specific temperature points without compromising the intake air temperature by IT hardware.
- Installation of variable frequency drivers to regulate temperature intervals and fan speeds.
-
Optimizing The Cooling Infrastructure
Photo Credit: 1.bp.blogspot.com
Installation of cooling units alone is not enough. Cooling iterations are necessary to achieve the optimal capacity of your cooling infrastructures. This can be done by interval checking of IT intake temperature relative to a particular temperature setpoint.
The principle is to optimize cooling to achieve the highest possible temperature while reducing fan speeds. Instantaneously, overseeing that IT intake air temperature should run within favorable limits is crucial.
It is also essential to run a good amount of cooling units. This process is needed to ensure that there is a constant cooling capacity to a data center. In unforeseen unit failure, there is still sufficient cooling support to sustain a specific temperature point.
Airflow Monitoring as Essential Activity
A data center’s reliability and safety come from a sound monitoring solution. As a vital part of data center management, monitoring should enable comprehensive tracking of environmental parameters in an IT environment.
AKCP Airflow Sensor
Some of the most basic monitoring tools, especially in airflow management, are airflow sensors. Detecting the presence or non-presence of airflow is necessary for the whole monitoring plan. AKCP airflow sensor can be placed in the air stream to monitor the status of flowing air. It is capable of alarm notification to gather the description and location of the fault.
Thermal Map Sensors
An airflow sensor complemented with specific thermal map sensors can eliminate hotspots on identified areas. AKCP thermal map connected to sensorProbe+ identifies any obstructions that impede airflow, causing high-temperature variance.
Even on sealed IT cabinets, AKCP thermal mapping can achieve a granular reading of temperature differential. Such reading will advise that proper airflow distribution is still maintained or lack thereof.
Quantifying Bypass Airflow
Bypass airflow challenges are present when running data centers. Because data centers derive power consumption, heat will be its by-product. Efforts to control the sources of heat have been a continuing hurdle for many data center managers.
Bypass airflow is just one of the many offshoot consequences in IT operations. Quantifying bypass airflow is hard. It is only in determining the actual value in the IT room we can carry through with our cooling strategies. This is where a sound monitoring setup comes into play. Once we determine some real numbers, such as bypass airflow, we get a clearer sense of direction on addressing it.
Bypass airflow can not be controlled on mere sealing or covering of air entries. It’s not that sealing does not have its merit. It gets the job done. But beyond the basic steps are opportunities for IT managers to be cost-efficient with their cooling methods. Improving cooling capacities refers to more than just the physical make-up of the whole data center system.
The real challenge in managing bypass airflow is understanding its nature. Reacting to a quantifiable number increases opportunities to better cooling strategies that do not break the bank. With these concrete numbers, we maintain a favorable IT equipment airflow volume while lowering cooling airflow volume that is bypass airflow.
Reference Links:
https://www.upsite.com/blog/bypass-airflow-simple-may-think/
https://www.anixter.com/content/dam/Suppliers/Upsite/Bypass%20Airflow%20Clarified%20White%20Paper.pdf